Industry News
Research, Science & Manufacturer Updates
Therapeutics Articles
An investigational, individualized neoantigen therapy, with personalized encoded mRNA, has demonstrated potential to enable patients’ immune systems to target cells that cause cancer.
Scientists at Harvard Medical School have developed a simple nasal spray, made of harmless ingredients, that can protect people against flu, colds and COVID-19 with near-100 percent success, and it costs just $25.
Immune globulin replacement and prophylactic antibiotics are commonly used to prevent infections in patients with secondary hypogammaglobulinemia due to hematological malignancies but have never been directly compared.
A new vaccine currently in development can effectively and affordably lower levels of “bad’ cholesterol in the body, a health problem that affects almost two in five adults in the U.S.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved two treatments, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, representing the first cell-based gene therapies for the treatment of sickle cell disease in patients 12 years and older.
CSL Behring is discontinuing all sizes of Hizentra vials in the U.S. by the end of September 2024.
Researchers have discovered a rare type of immune cell that may predict how likely some patients with skin cancer will respond to immunotherapy treatment.
Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust has enrolled the first United Kingdom (UK) patients who have received an experimental messenger RNA (mRNA) therapy — a type of immunotherapy treatment called mRNA-4359 — in its Phase I/II clinical trial.
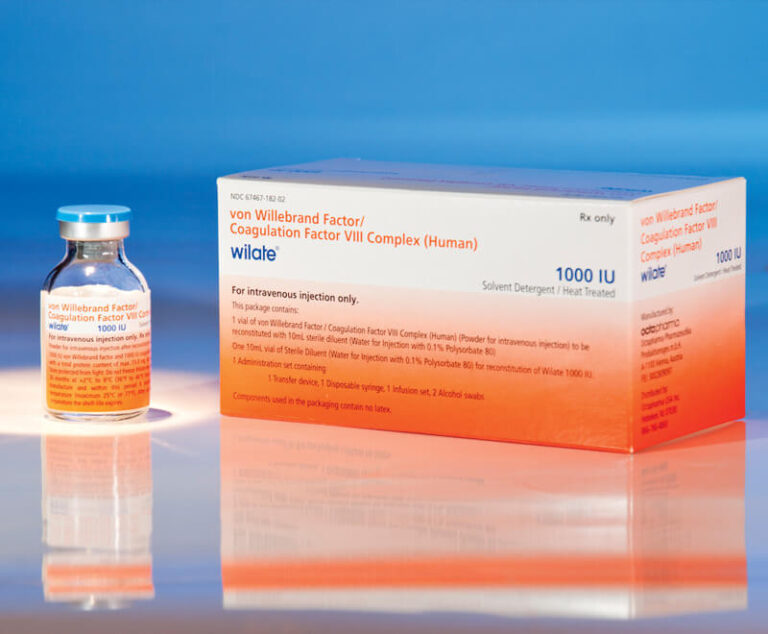
Octapharma USA's wilate, von Willebrand factor (VWF)/coagulation factor VIII complex (human) lyophilized power for solution for intravenous injection, has been given expanded approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for routine prophylaxis to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in adults and children aged 6 and older with any type of von Willebrand disease (VWD).
In a study, researchers found that fSCIG 10% was more effective in preventing CIDP relapse than placebo, supporting its potential use as maintenance CIDP treatment.
A team of Australian investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study to determine whether there is a significant benefit in more severely affected cases regularly infused with albumin.
An international early-phase clinical trial has found a "two-for-one" cancer immunotherapy, tebotelimab, is potentially more effective and at least as safe as standard immunotherapies.